Anatomical Registration
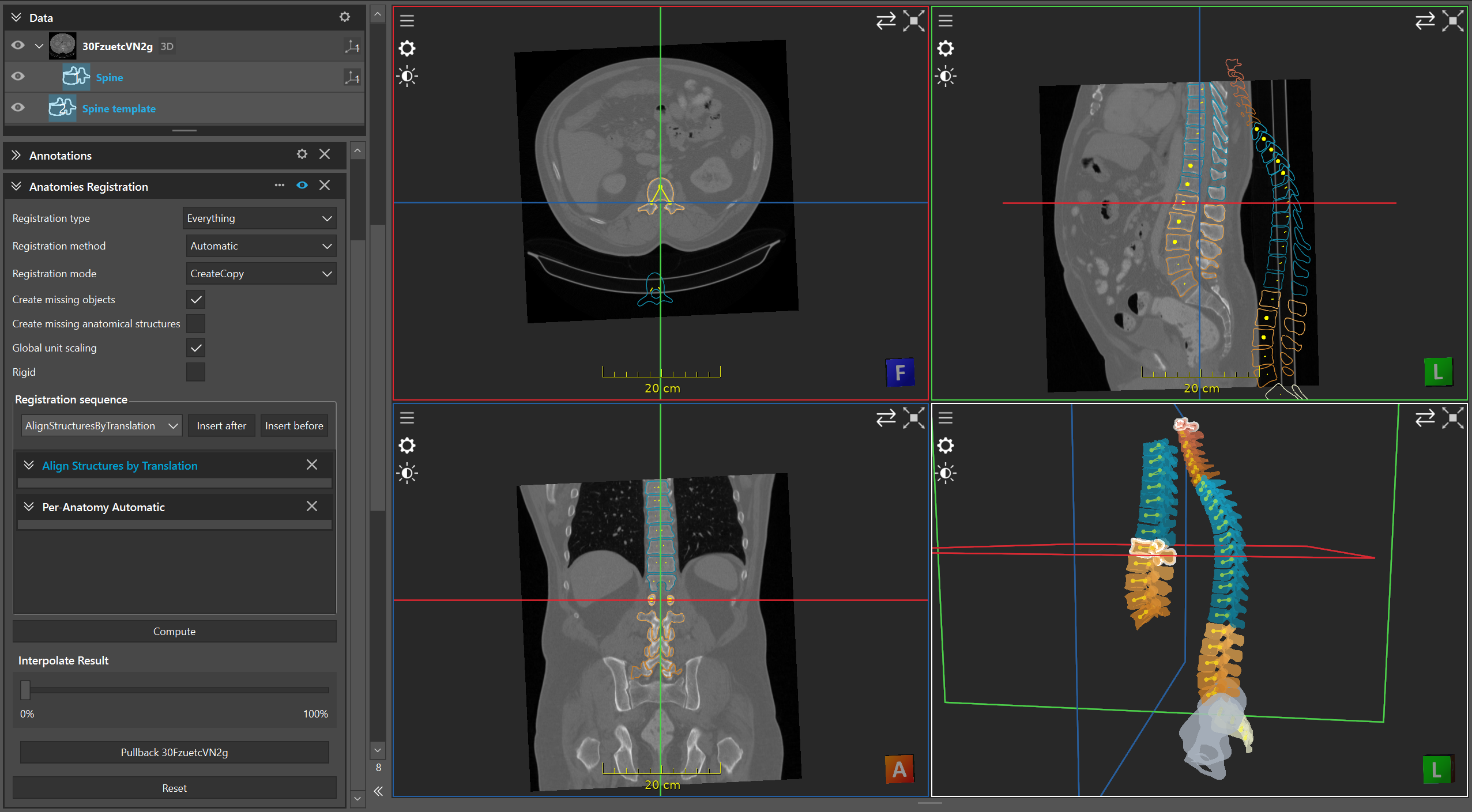
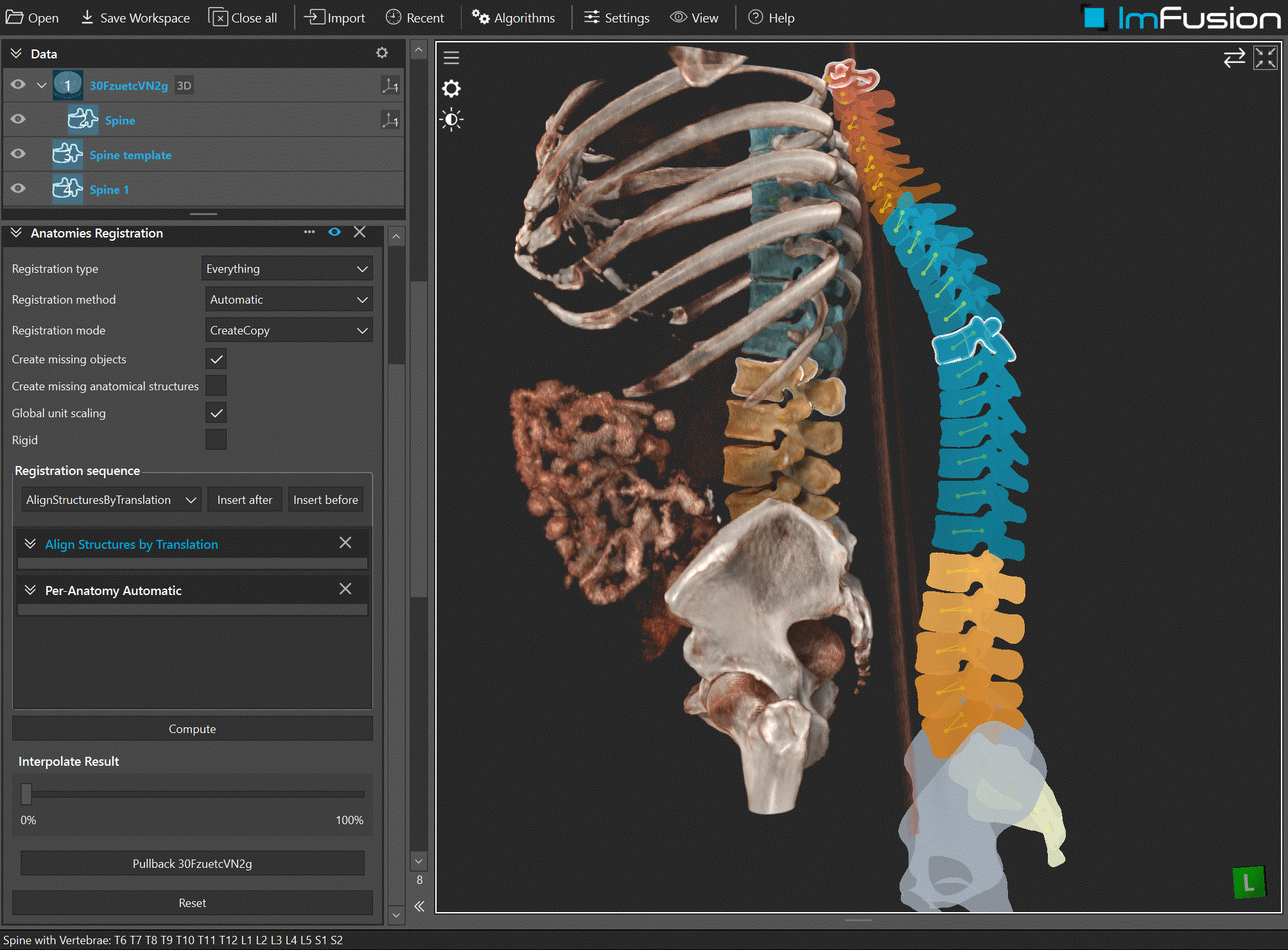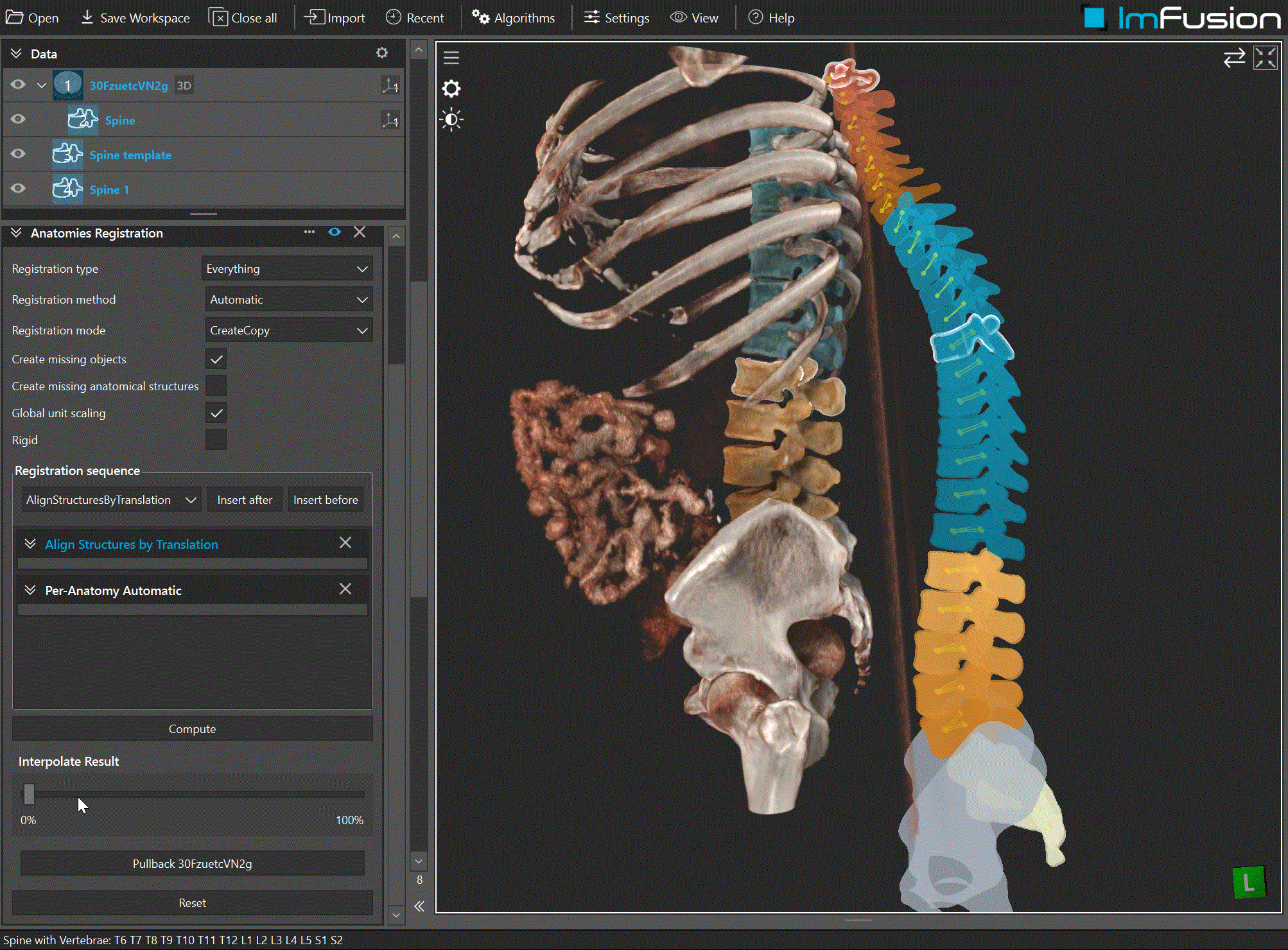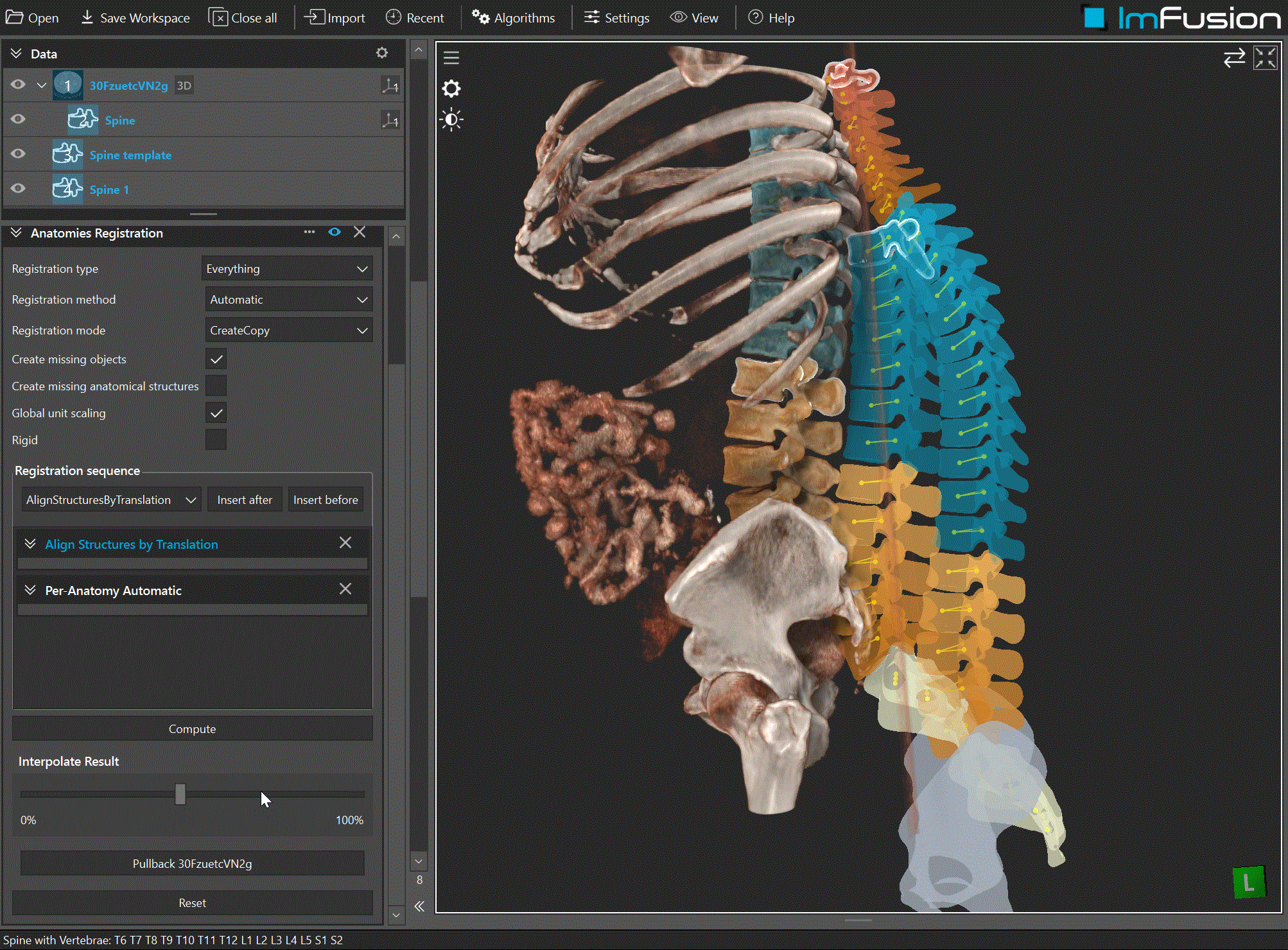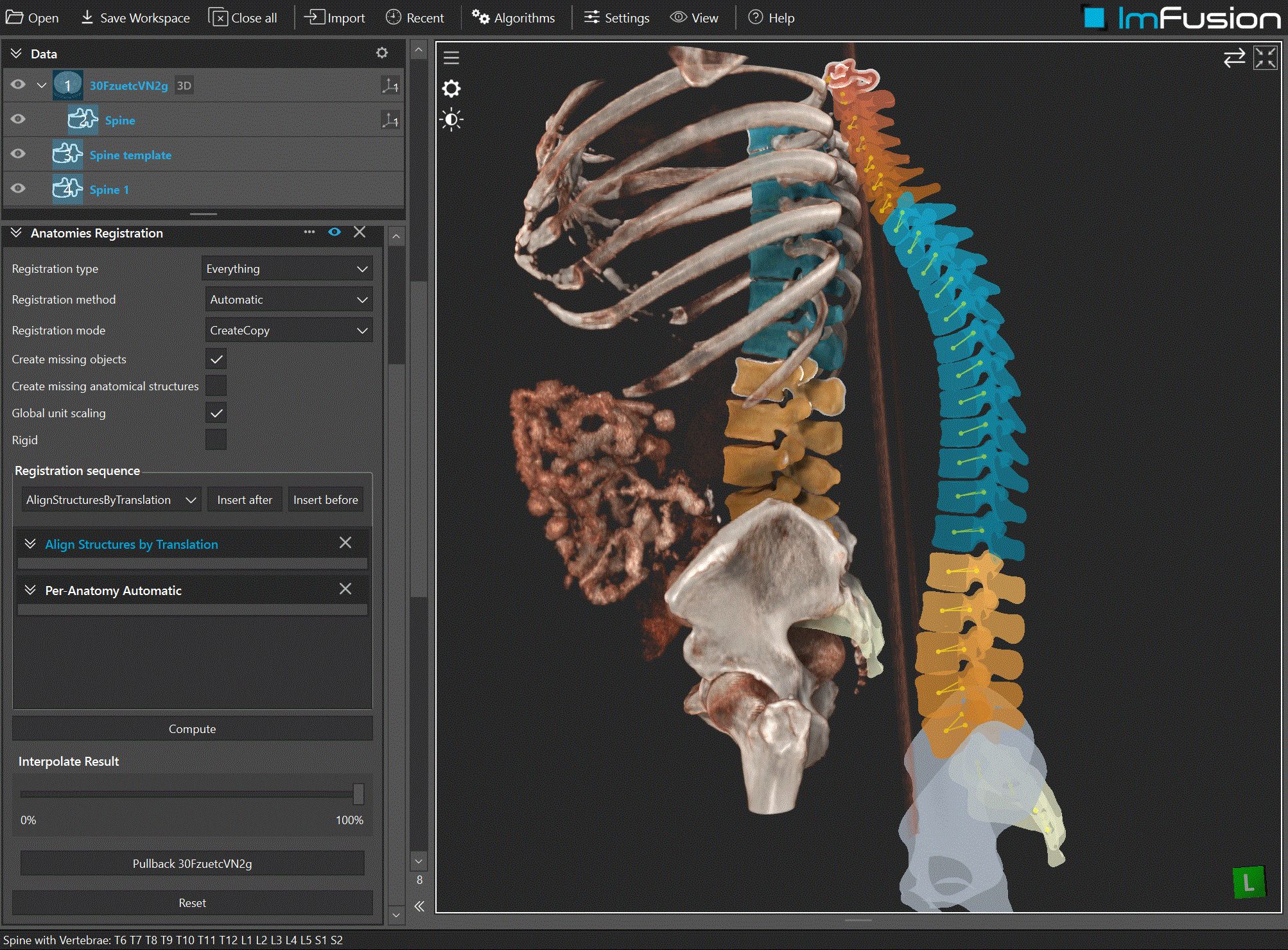
Overview
Conceptual overview of registering one AnatomicalStructureCollection (ASC) to another via ASC Registration.
Outcomes
Updated moving ASC pose and optional per-structure transformations.
Modes and pipeline
Default modes:
AlignStructuresByTranslationaligns each matching structure using the vector between corresponding centroids or keypoints (fast coarse initialization).Automaticselects a reasonable multi-stage pipeline based on available data.Custom pipeline: override behavior per structure using a
Modify Structurestep, then attach different registration modes to the modified subset (e.g., rigid ICP for vertebrae, translation-only for ribs). You can also choose whether structures contribute to registration (used to compute transformations) and whether they are transformed (not frozen). Pipelines execute in sequence and can mix global and per-structure operations. It is for instance possible to initialize globally based on one anatomical structure, while still registering all structures present in the moving ASC.
Registration data and propagation
Data used:
Geometry: meshes and/or keypoints per structure are primary inputs. Meshes are aligned via distance-based surface matching; keypoints/points can be aligned with ICP or centroid initialization.
Meshes: meshes are aligned via distance-based surface matching.
Images: if present, image-based refine uses intensity similarity around structures.
Label maps: are not registered directly.
Associations: matching by structure identifiers determines correspondences.
Propagation of results:
Global transform: if a global alignment is estimated, it is applied to the moving ASC root.
Per-structure transforms: when modes operate per structure, transforms are stored with each structure and applied to their attached data (meshes, keypoints, planes, splines, point clouds) consistently. If attached data are outside the structure, the transformation is extrapolated.
Frozen structures: structures can be marked as frozen, meaning they are not transformed during registration.
Options to create and propagate missing data:
Create missing structures: structures present in the moving ASC but absent in the fixed ASC are kept in the output and created if needed. When no per-structure deformation is available, the global linear part of the registration is used to place them.
Create missing objects: within each structure, missing objects (e.g., meshes, keypoints, planes, point clouds, images) are created and transformed based on the registration result. If disabled, only existing objects are updated; missing ones are left empty. This allows propagation of data such as keypoints from a template to the subject image.
These options affect only the output ASC produced by the registration step. They do not alter the input ASCs.
Frozen structures are never transformed, even if creation options are enabled.
See also
ASC Registration for the registration algorithm used
Anatomical Structure Collection (ASC) for the underlying data model