Building data pipelines with the ImFusion Python SDK
The imfusion.machinelearning.Dataset class offers a high-level API for constructing a data loading and processing pipeline. After specifying the file specification upon instantiation, the pipeline can be customized using a set of decorator methods. Each such method adds a modular processing step to the pipeline. It also returns a reference to self so the entire pipeline can be conveniently specified using method chaining.
[ ]:
import _engine_plugin_guard
import imfusion
import imfusion.machinelearning as ml
from pathlib import Path
from demo_utils import mpr_plot, unzip_folder
unzipped_folder = unzip_folder('data/pet-ct-rtstruct.zip')
[ ]:
# The data we are going to use for this example
ct_file = Path('data/pet-ct-rtstruct/ct.imf').absolute().as_posix()
target_file = Path('data/pet-ct-rtstruct/bones.imf').absolute().as_posix()
[3]:
# Loading the images just so we can visualize them here
# This has no relevance to the pipeline that we will construct below
mpr_plot(
imfusion.load(ct_file)[0][0],
labels=imfusion.load(target_file)[0][0],
vmin=-500,
vmax=1000,
label_alpha=0.2
)
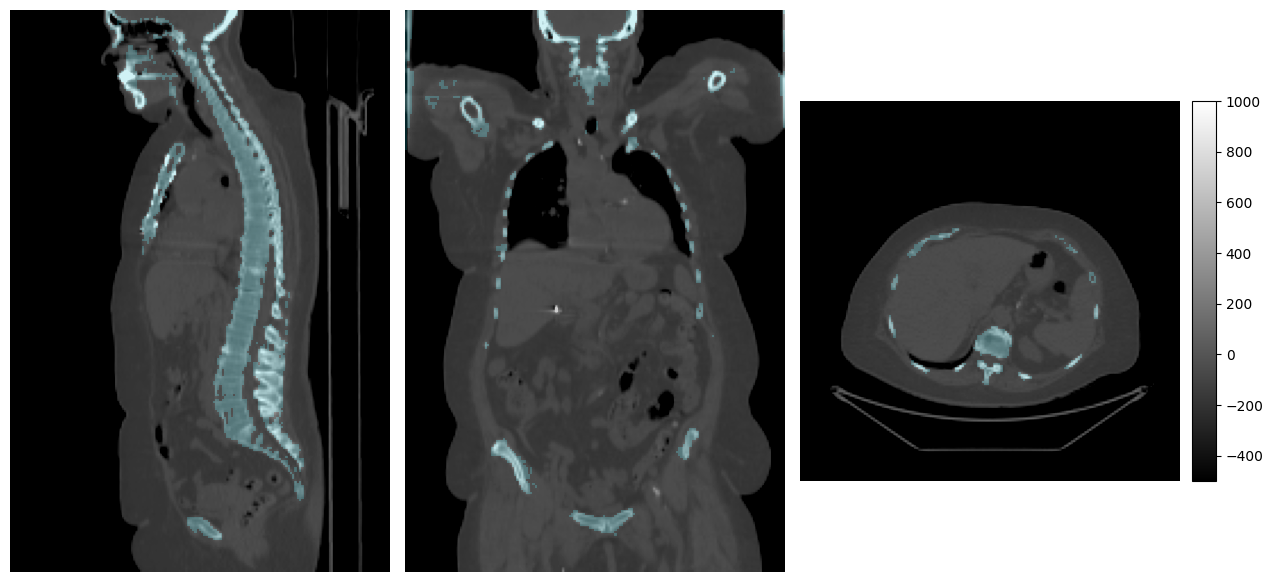
The class representing our data-loading pipeline is imfusion.machinelearning.Dataset. We can construct an instance by giving it a specification that details how to load data from disk. Afterward, we can attach additional processing using its methods. These also permit method-chaining. Among them, preprocess allows to leverage Operations to apply all kinds of transformations on the data.
[4]:
# Since each file may contain multiple images we have to specify a mapping in our file loading specification
# Each mapping takes the form <image-index-in-file> -> <field-name-in-the-data-item-after-loading>
ct_loading_spec = ({0: 'images'}, [ct_file])
target_loading_spec = ({0: 'target'}, [target_file])
# We construct the dataset by passing it a list of file loading specifications
# Optionally, we can also enable additional logging by setting verbose=True
dataset = ml.Dataset([ct_loading_spec, target_loading_spec], verbose=True)
# Now we can build the pipeline using method chaining
dataset = (
dataset
.preprocess([ # applies some deterministic processing to every loaded item
ml.MarkAsTargetOperation(apply_to=["target"]),
ml.MakeFloatOperation(),
ml.NormalizePercentileOperation(min_percentile=0.01, max_percentile=0.99),
ml.ResampleOperation(resolution=[3]*3, preserve_extent=True),
])
.memory_cache() # caches preprocessed items in memory, so we don't need to repeat the steps before
.repeat(1_000) # repeats the entire pipeline (we use it here since we are working with only one sample)
.preprocess([ # add some non-deterministic augmentation, by default all are applied but this can be tuned with the `probability` kw-argument
ml.RandomRotationOperation(angles_range=[10,10,10]),
ml.RandomGammaCorrectionOperation(random_range=0.2),
ml.BakeTransformationOperation(),
])
.sample( # samples a region of interest from the item
samplers=[ # we can specify multiple sampling strategies which will be chosen at random
ml.RandomROISampler(roi_size=[128]*3), # this samples a random 128³ sub-region
ml.LabelROISampler(roi_size=[128]*3, labels_values=[1], sample_boundaries_only=True) # similar to RandomROISampler but ensures that the target is visible
],
weights=[1, 2] # specifies the weights for the random choice of the sampling strategy
)
.batch(2) # batches inputs in pairs
)
Now that we have created the pipeline we can get items from it using iter / next (or for-loops which use those implicitly) The output of the pipeline is always a DataItem, which is a mapping from a string identifier to a piece of processed data.
[5]:
imfusion.set_log_level(2)
sample = next(dataset)
sample
[ML.FileReader] Loading /data/imfusion/public-python-demos/imfusion_sdk/data/pet-ct-rtstruct/ct.imf
[ML.FileReader] Loading /data/imfusion/public-python-demos/imfusion_sdk/data/pet-ct-rtstruct/bones.imf
[ML.FileReader] next() executed in 19.507 ms
[ML.OperationsSequence] MarkAsTargetOperation executed in 0.003 ms
[ML.OperationsSequence] MakeFloatOperation executed in 8.513 ms
[ML.OperationsSequence] NormalizePercentileOperation executed in 8.895 ms
[ML.OperationsSequence] ResampleOperation executed in 0.963 ms
[ML.CacheDataLoader] next() executed in 37.858 ms
[ML.RepeatDataLoader] next() executed in 75.816 ms
[ML.OperationsSequence] RandomRotationOperation executed in 0.080 ms
[ML.OperationsSequence] RandomGammaCorrectionOperation executed in 2.194 ms
[ML.OperationsSequence] BakeTransformationOperation executed in 4.297 ms
[ML.MapDataLoader] next() executed in 34.662 ms
[ML.CacheDataLoader] next() executed in 7.678 ms
[ML.CacheDataLoader] next() executed in 0.015 ms
[ML.RepeatDataLoader] next() executed in 0.002 ms
[ML.OperationsSequence] RandomRotationOperation executed in 0.079 ms
[ML.OperationsSequence] RandomGammaCorrectionOperation executed in 16.339 ms
[ML.OperationsSequence] BakeTransformationOperation executed in 7.795 ms
[ML.MapDataLoader] next() executed in 31.064 ms
[ML.BatchDataLoader] next() executed in 0.287 ms
[ML.Dataset] next() executed in 180.417 ms
[5]:
imfusion.machinelearning.DataItem({images: imfusion.machinelearning.ImageElement(imfusion.SharedImageSet(size: 2, [
imfusion.SharedImage(FLOAT width: 128 height: 128 slices: 128 spacing: 2.95408x2.97105x2.956 mm),
imfusion.SharedImage(FLOAT width: 128 height: 128 slices: 128 spacing: 2.95996x2.96202x2.9715 mm)
])), target: imfusion.machinelearning.ImageElement(imfusion.SharedImageSet(size: 2, [
imfusion.SharedImage(UBYTE width: 128 height: 128 slices: 128 spacing: 2.95408x2.97105x2.956 mm),
imfusion.SharedImage(UBYTE width: 128 height: 128 slices: 128 spacing: 2.95996x2.96202x2.9715 mm)
]))})
[6]:
mpr_plot(
sample["images"].content[0],
labels=sample["target"].content[0],
)
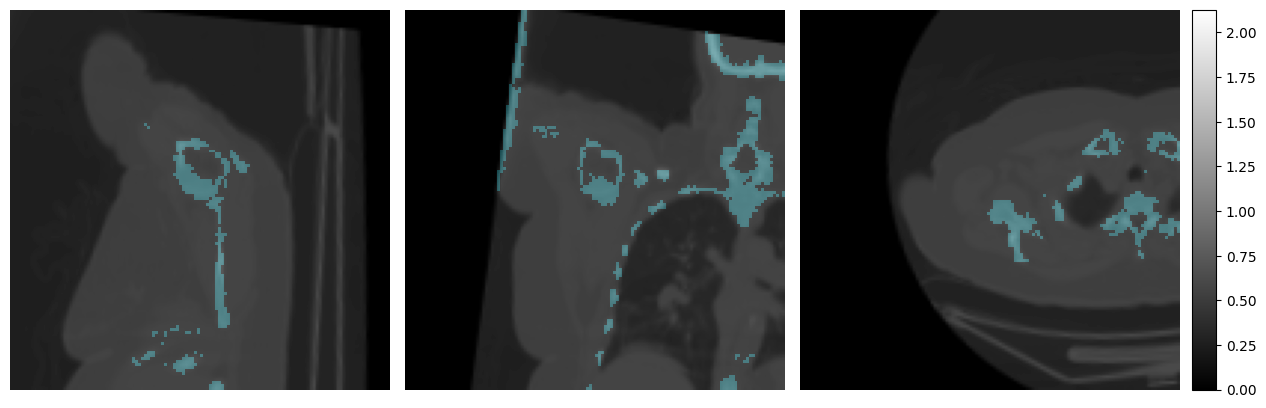
Notice how the loading is much faster the second time due to the caching.
[7]:
next(dataset)
[ML.CacheDataLoader] next() executed in 3.440 ms
[ML.CacheDataLoader] next() executed in 0.019 ms
[ML.RepeatDataLoader] next() executed in 0.002 ms
[ML.OperationsSequence] RandomRotationOperation executed in 0.067 ms
[ML.OperationsSequence] RandomGammaCorrectionOperation executed in 23.197 ms
[ML.OperationsSequence] BakeTransformationOperation executed in 6.874 ms
[ML.MapDataLoader] next() executed in 0.898 ms
[ML.CacheDataLoader] next() executed in 2.933 ms
[ML.CacheDataLoader] next() executed in 0.013 ms
[ML.RepeatDataLoader] next() executed in 0.001 ms
[ML.OperationsSequence] RandomRotationOperation executed in 0.080 ms
[ML.OperationsSequence] RandomGammaCorrectionOperation executed in 11.837 ms
[ML.OperationsSequence] BakeTransformationOperation executed in 6.887 ms
[ML.MapDataLoader] next() executed in 38.669 ms
[ML.BatchDataLoader] next() executed in 0.316 ms
[ML.Dataset] next() executed in 95.362 ms
[7]:
imfusion.machinelearning.DataItem({images: imfusion.machinelearning.ImageElement(imfusion.SharedImageSet(size: 2, [
imfusion.SharedImage(FLOAT width: 128 height: 128 slices: 128 spacing: 2.94908x2.9728x2.9629 mm),
imfusion.SharedImage(FLOAT width: 128 height: 128 slices: 128 spacing: 2.98749x2.9684x2.98042 mm)
])), target: imfusion.machinelearning.ImageElement(imfusion.SharedImageSet(size: 2, [
imfusion.SharedImage(UBYTE width: 128 height: 128 slices: 128 spacing: 2.94908x2.9728x2.9629 mm),
imfusion.SharedImage(UBYTE width: 128 height: 128 slices: 128 spacing: 2.98749x2.9684x2.98042 mm)
]))})
Since we are working with ImFusion Data subclasses, attached metadata is persistent through the entire pipline. Some is even generated by the pipeline itself to facilitate debugging and compliance.
For example the ProcessingRecordDataComponent records all operations (and their configuration) that have acted on this piece of data.
[8]:
sample['images'].components.processing_record.configuration().asdict()
[8]:
{'0/0': {'MakeFloatOperation/0': {'device': EnumStringParam assigned to GPUIfOpenGl in {ForceGPU; GPUIfOpenGl; GPUIfGlImage; ForceCPU},
'processing_policy': 0,
'seed': 1,
'error_on_unexpected_behaviour': False},
'NormalizePercentileOperation/0': {'device': EnumStringParam assigned to GPUIfOpenGl in {ForceGPU; GPUIfOpenGl; GPUIfGlImage; ForceCPU},
'processing_policy': 0,
'seed': 1,
'error_on_unexpected_behaviour': False,
'ignore_zeros': False,
'clamp_values': False,
'max_percentile': 0.990000009536743,
'min_percentile': 0.00999999977648258},
'ResampleOperation/0': {'device': EnumStringParam assigned to GPUIfOpenGl in {ForceGPU; GPUIfOpenGl; GPUIfGlImage; ForceCPU},
'processing_policy': 1,
'seed': 1,
'error_on_unexpected_behaviour': False,
'preserve_extent': True,
'resolution': '3 3 3 '},
'RotationOperation/0': {'device': EnumStringParam assigned to GPUIfOpenGl in {ForceGPU; GPUIfOpenGl; GPUIfGlImage; ForceCPU},
'processing_policy': 1,
'seed': 1,
'error_on_unexpected_behaviour': False,
'adjust_size': False,
'apply_now': False,
'angles': '5.05846214294434 -8.43384456634521 5.46281337738037 '},
'GammaCorrectionOperation/0': {'device': EnumStringParam assigned to GPUIfOpenGl in {ForceGPU; GPUIfOpenGl; GPUIfGlImage; ForceCPU},
'processing_policy': 0,
'seed': 1,
'error_on_unexpected_behaviour': False,
'gamma': 1.10116934776306},
'BakeTransformationOperation/0': {'device': EnumStringParam assigned to GPUIfOpenGl in {ForceGPU; GPUIfOpenGl; GPUIfGlImage; ForceCPU},
'processing_policy': 1,
'seed': 1,
'error_on_unexpected_behaviour': False},
'CropOperation/0': {'device': EnumStringParam assigned to GPUIfOpenGl in {ForceGPU; GPUIfOpenGl; GPUIfGlImage; ForceCPU},
'processing_policy': 1,
'apply_to': ['sis'],
'error_on_unexpected_behaviour': False,
'offset': '5 57 149 ',
'size': '128 128 128 '},
'LabelROISampler/0': {'device': EnumStringParam assigned to GPUIfOpenGl in {ForceGPU; GPUIfOpenGl; GPUIfGlImage; ForceCPU},
'processing_policy': 1,
'seed': 1,
'error_on_unexpected_behaviour': False,
'sample_boundaries_only': True,
'fallback_to_random': True,
'labels_values': [1],
'roi_size': '128 128 128 ',
'label_padding_mode': EnumStringParam assigned to clamp in {clamp; mirror; zero},
'padding_mode': EnumStringParam assigned to clamp in {clamp; mirror; zero}}}}
We can use this to verify that the target was indeed not modified by our random augmentations.
[9]:
sample['target'].components.processing_record.configuration().asdict()
[9]:
{'0/0': {'ResampleOperation/0': {'device': EnumStringParam assigned to GPUIfOpenGl in {ForceGPU; GPUIfOpenGl; GPUIfGlImage; ForceCPU},
'processing_policy': 1,
'seed': 1,
'error_on_unexpected_behaviour': False,
'preserve_extent': True,
'resolution': '3 3 3 '},
'RotationOperation/0': {'device': EnumStringParam assigned to GPUIfOpenGl in {ForceGPU; GPUIfOpenGl; GPUIfGlImage; ForceCPU},
'processing_policy': 1,
'seed': 1,
'error_on_unexpected_behaviour': False,
'adjust_size': False,
'apply_now': False,
'angles': '5.05846214294434 -8.43384456634521 5.46281337738037 '},
'BakeTransformationOperation/0': {'device': EnumStringParam assigned to GPUIfOpenGl in {ForceGPU; GPUIfOpenGl; GPUIfGlImage; ForceCPU},
'processing_policy': 1,
'seed': 1,
'error_on_unexpected_behaviour': False},
'CropOperation/0': {'device': EnumStringParam assigned to GPUIfOpenGl in {ForceGPU; GPUIfOpenGl; GPUIfGlImage; ForceCPU},
'processing_policy': 1,
'apply_to': ['sis'],
'error_on_unexpected_behaviour': False,
'offset': '5 57 149 ',
'size': '128 128 128 '},
'LabelROISampler/0': {'device': EnumStringParam assigned to GPUIfOpenGl in {ForceGPU; GPUIfOpenGl; GPUIfGlImage; ForceCPU},
'processing_policy': 1,
'seed': 1,
'error_on_unexpected_behaviour': False,
'sample_boundaries_only': True,
'fallback_to_random': True,
'labels_values': [1],
'roi_size': '128 128 128 ',
'label_padding_mode': EnumStringParam assigned to clamp in {clamp; mirror; zero},
'padding_mode': EnumStringParam assigned to clamp in {clamp; mirror; zero}}}}
Another example of metadata that we would like to keep throughout the pipeline is licensing information of the data.
In this example the loaded data already comes with a DatasetLicenseComponent
[10]:
sample['images'].components.dataset_license
[10]:
DatasetLicenseComponent(infos=[
DatasetLicenseComponent.DatasetInfo(
name=The Clinical Proteomic Tumor Analysis Consortium Uterine Corpus Endometrial Carcinoma Collection (CPTAC-UCEC),
authors=National Cancer Institute Clinical Proteomic Tumor Analysis Consortium (CPTAC),
website=https://doi.org/10.7937/K9/TCIA.2018.3R3JUISW,
license=CC BY 3.0,
attribution_required=true,
commercial_use_allowed=true
),
DatasetLicenseComponent.DatasetInfo(
name=The Clinical Proteomic Tumor Analysis Consortium Uterine Corpus Endometrial Carcinoma Collection (CPTAC-UCEC),
authors=National Cancer Institute Clinical Proteomic Tumor Analysis Consortium (CPTAC),
website=https://doi.org/10.7937/K9/TCIA.2018.3R3JUISW,
license=CC BY 3.0,
attribution_required=true,
commercial_use_allowed=true
) ])
The data can then be easily converted to torch and then fed into your ML model (but this loses any metadata). (The cells below only work if you also install the torch package: pip install 'torch==2.2.2. We did not include it in the requirements due to the massive file size)
[11]:
tensor = sample['images'].torch(device='cpu')
tensor.shape
[11]:
torch.Size([2, 1, 128, 128, 128])
And we can easily convert torch tensors back to ImFusion types. If we provide an existing image as a template, we can also copy over its metadata. This comes in handy when we want to e.g. convert the output of a ML model back to a SharedImageSet and retain the metadata of the input to the model.
[12]:
roundtrip = imfusion.SharedImageSet.from_torch(tensor, get_metadata_from=sample['images'].sis)
assert roundtrip.components.dataset_license == sample['images'].components.dataset_license
roundtrip
[12]:
imfusion.SharedImageSet(size: 2, [
imfusion.SharedImage(FLOAT width: 128 height: 128 slices: 128 spacing: 2.95408x2.97105x2.956 pix),
imfusion.SharedImage(FLOAT width: 128 height: 128 slices: 128 spacing: 2.95996x2.96202x2.9715 pix)
])