 |
ImFusion C++ SDK 4.4.0
|
 |
ImFusion C++ SDK 4.4.0
|
Tomographic reconstruction techniques to compute the 3D CT images from a set of X-ray projections in different acquisition geometries. More...
Tomographic reconstruction techniques to compute the 3D CT images from a set of X-ray projections in different acquisition geometries.
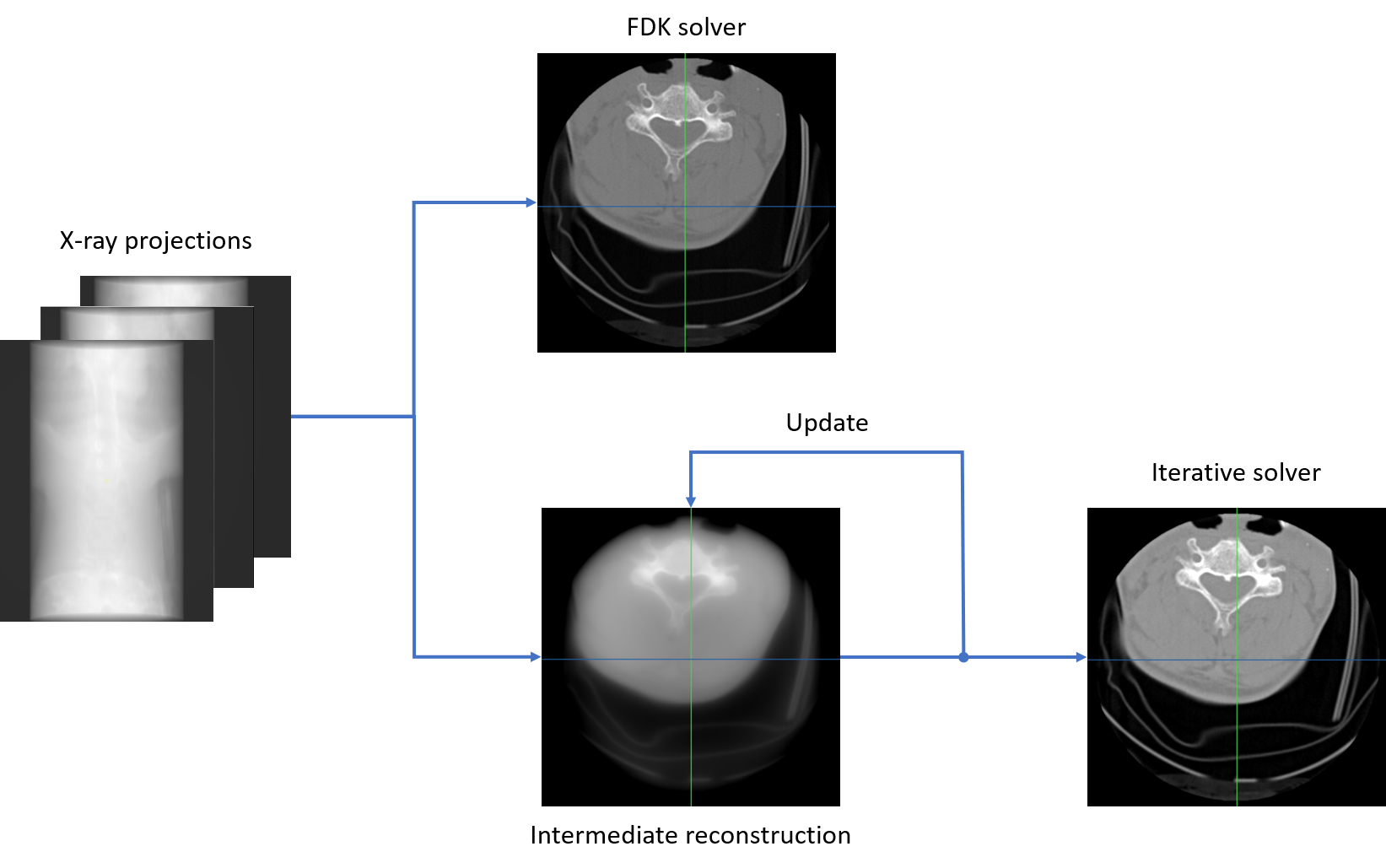
This page will provide a brief overview of how to use ReconstructionAlgorithm class to compute an X-ray tomographic image from a given ConeBeamData instance. A ConeBeamData object refers to a set of X-ray projections acquired with a point source. Additionally, the ConeBeamData class also attaches a ConeBeamGeometry instance to describe the acquisition geometry of a cone-beam CT system. In the following tutorial, the ConeBeamGeometry is assumed to have been calibrated.
CT reconstruction can be computed using different mathematical approaches. The current ReconstructionAlgorithm class supports to various formulations of the reconstruction problem through the problem mode and uses different techniques to solve the corresponding problem by setting the solver mode. To begin, one need to first create a ReconstructionAlgorithm instance which takes a ConeBeamData as input.
Once initialized, the ReconstructionAlgorithm creates a SharedImageSet instance to store the reconstructed data. Now, we will specify the ImageDescriptorWorld for the reconstruction volume.
The problem and solver mode must be set up in such a way that they are comparable. Currently supported reconstruction problems include "LeastSquaresProblem", "StatisticallyWeightedLeastSquaresProblem", "LeastSquaresIsotropicTV", "DummyDevelopmentProblem", "none". And supported solvers include "FDK", "MLEM", "CG", "SART", "SQS", "none". Not all solvers are comparible to every problem, set the problem first, then the solver. If the problem and the solver are mismatched, the solver will be reset to a compatible solver on changes of the problem, see ReconstructionAlgorithm.
Depending on the problem and solver, additional configurations can be specified through the corresponding algorithm parameters. There are several configurations that are only available for specific solver. One can set them through the corresponding solver instance. For example, we can set the p_subsetSize and p_additionalWeights paramters for the FDK solver as follows. Different additional weights can be used: "None", "Parker", "Wang", "ParkerAndWang". Enable/disable FDK p_normalize parameter that will normlize the final reconstruction with the number of rays passing through each voxel.
The iterative solvers require p_maxIterations parameter to be set along with the other parameters:
We can now run the ReconstructionAlgorithm to compute the CT image from the input data with specified volume descriptor, and take the output CT volume as a SharedImageSet instance.
Topics | |
| CT Solver | |
| CT Event Handler | |
Classes | |
| class | ImFusion::CT::CBCTPostProcessing |
| CBCTPostProcessing performs a cone cropping of a CT volume. More... | |
| class | ImFusion::CT::ConeBeamReconLoaderExtra |
| Loading and pre-processing of data from various CBCT devices. More... | |
| class | ImFusion::CT::GlFourierFilter1D |
| OpenGL-based 1D ramp filter for FDK reconstruction. More... | |
| class | ImFusion::CT::ProjectionSets |
| Computation of projection subsets for iterative reconstruction. More... | |
| class | ImFusion::CT::CBCTProjector |
| Abstract base class for Cone-Beam Computed Tomography (CBCT) projectors. More... | |
| class | ImFusion::CT::GlCBCTProjector |
| OpenGL-based cone-beam CT projector implementation. More... | |
| class | ImFusion::CT::ReconstructionAlgorithm |
| Algorithm for tomographic reconstruction. More... | |
| class | ImFusion::CT::AlgorithmReconstructionDecoratorInterface |
| Base class interface for AlgorithmReconstructionDecorator. More... | |
| class | ImFusion::CT::AlgorithmReconstructionDecorator< Base > |
| Template decorator for algorithms requiring reconstruction capabilities. More... | |